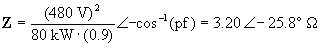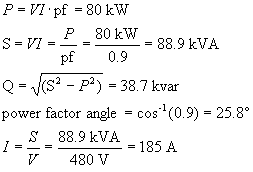MEL TECH
CIRCTRONICS
What is power factor?
Power factor is the relationship between working (active) power and total power absorbed (apparent power). Power factor is a measurement of how effectively electrical power is being used. The higher the power factor, the more effectively electrical power is being used.
A distribution system's operating power is composed of two parts: Active (working) power and reactive (non-working magnetizing) power. The ACTIVE power performs the useful work - the REACTIVE power does not. It's only function is to develop magnetic fields required by inductive devices.
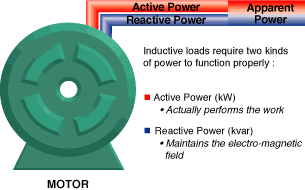
Why improve low power factor?
Low power factor means poor electrical efficiency. The lower the power factor, the higher the apparent power drawn from the distribution network.
Example:
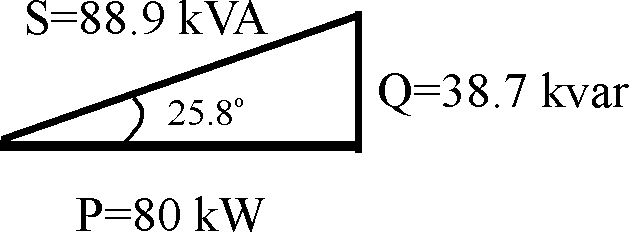
1) Draw the power triangle for a single-phase source which delivers 80 kW to a load at 0.7 pf lagging. If the source voltage is 480 V, calculate the current required by this load.
Solution:
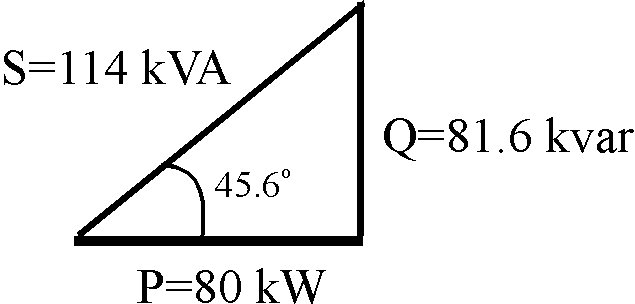

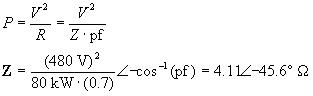
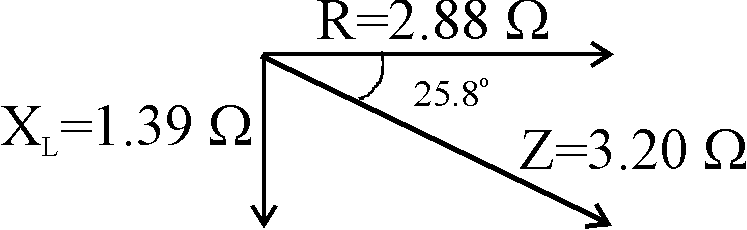
This impedance contains resistive and inductive elements

R = 2.88 OHMS
XL = 2.94 OHMS