

MEL TECH
CIRCTRONICS
Ohm's Law is one of the most fundamental law in electrical circuits relating voltage, current, and resistance. This law was developed in 1827 by German Physicist George Simon Ohm (1787 - 1854).
DC CIRCUITS
OHM'S LAW

According to Ohm's law, the current (I) flowing in an electrical circuit is directly proportional to the applied voltage (V) and inversely proportional to the equivalent resistance (R) of the said circuit. Mathematically,


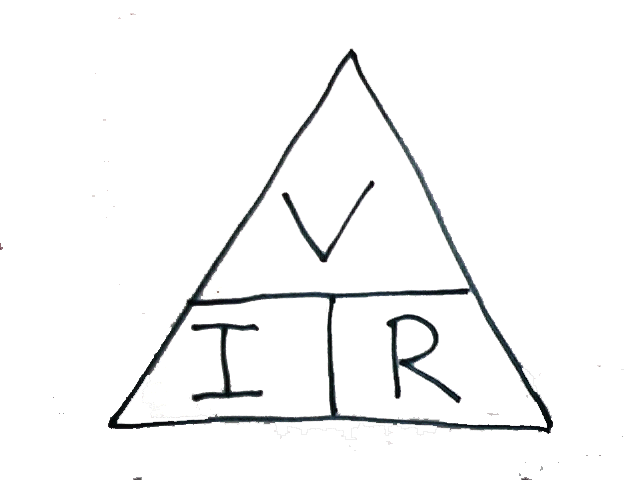
The VRI triangle:
Where:
V - applied voltage (Volt)
R - resistance of the circuit (Ohm)
I - current drawn (Ampere)
Example:

If V = 9V and R = 1000 Ohms, I is
I = V / R
= 9V / 1000 Ω
I = 0.009 A or 9mA (milliamperes)
If R = 100 Ω and I = 0.09A, V is
V = I R
= (0.09A) x (100 Ω)
V = 9V
If V = 9V and I = 0.05a, R is
R = V / I
= 9V / 0.05A
R = 180 Ω