

MEL TECH
CIRCTRONICS
Electrical Power
Electrical Power - the rate at which electrical energy is used or consumed.
Watt - the unit of electrical power, equicvalent to one joule of energy consumed in one second (W = J / s). Named after the Scottish Engineer and inventor James Watt (1736 - 1819).

Where:
P - electrical power (Watt)
V - voltage (Volt)
I - current (Ampere)
R - resistance (Ohm)
The details of the units are as follows:
Example:


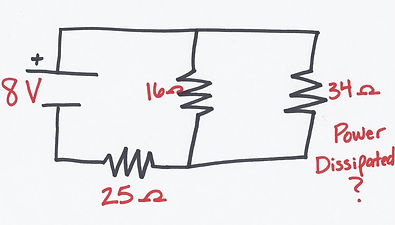
Since 16 Ω and 34 Ω are parallel, we can use:
16 Ω||34 Ω = _(16 Ω)(34)
16 Ω + 34 Ω
= 10.88 Ω
Since 10.88 Ω and 25 Ω are in series:
Req = 10.88 Ω + 25 Ω
Req = 35.88 Ω
Then, solve for the current (I),
I = V / Req
= 8 / 35.88 Ω
I = 0.223 A
Lastly, Solve for Power,
P = I V
= (0.223A) x (8V)
P = 1.78 W